Hemorrhoids Best Treatment From Dr. Anuj Tyagi
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lower part of the rectum or anus. They can be internal or external and are a common condition affecting many people.
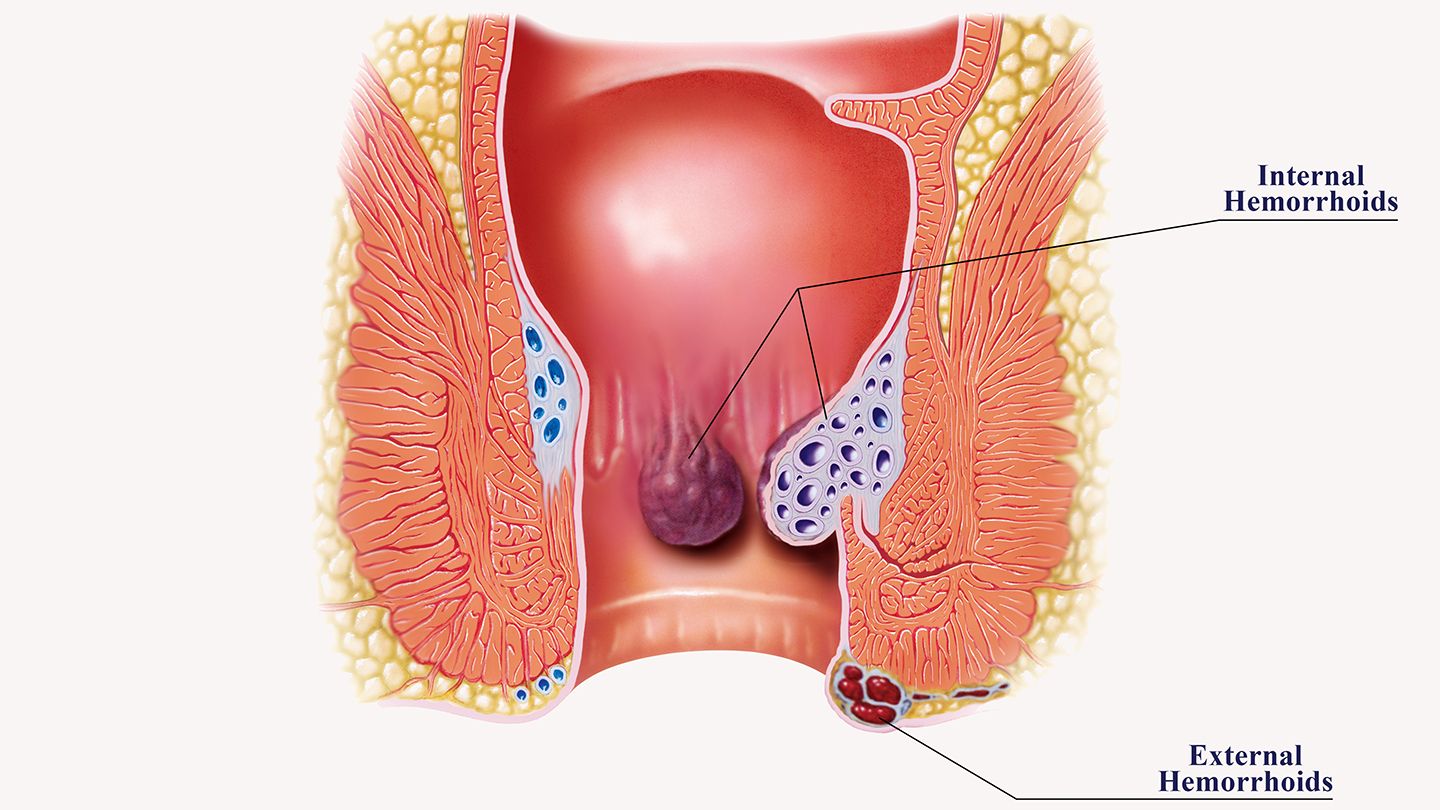
Internal hemorrhoids develop inside the rectum and are not usually visible, but they can cause painless bleeding during bowel movements. External hemorrhoids are located outside the anus and can be seen or felt as a lump or swelling around the anus. They can be painful and itchy and may also bleed.
Hemorrhoids can be caused by a variety of factors, including straining during bowel movements, sitting for long periods, chronic constipation or diarrhea, obesity, and pregnancy. Treatment options range from lifestyle changes such as increasing fiber intake and drinking plenty of fluids, to topical treatments such as creams and ointments, and in severe cases, surgery.
Symptoms
The symptoms of hemorrhoids can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. The following are some common symptoms of hemorrhoids:
- Itching, burning, or irritation in the anal region
- Pain or discomfort during bowel movements
- Bright red blood on the toilet paper or in the toilet bowl after a bowel movement
- Swelling or a lump near the anus
- Leakage of feces or mucus from the anus
- Pain or discomfort in the anal region, especially when sitting or standing for long periods
Internal hemorrhoids may not cause any symptoms, but they can cause painless bleeding during bowel movements. External hemorrhoids may cause more discomfort and pain than internal hemorrhoids, and they can be felt as a lump or swelling around the anus.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it's important to talk to your doctor to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment options.
Thrombosed Hemorrhoids
Thrombosed hemorrhoids are a type of hemorrhoid that develops when a blood clot forms within the swollen vein in the anal region. They can occur both internally and externally and are often characterized by severe pain and discomfort.
The symptoms of thrombosed hemorrhoids may include:
- Swelling or a hard lump around the anus
- Intense pain or discomfort, especially during bowel movements or when sitting
- Itching or burning in the affected area
- Bleeding, usually small amounts
When To See a Doctor
It is recommended to see a doctor if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Bleeding during bowel movements that does not stop or recurs frequently
- Severe pain or discomfort in the anal region
- Prolapsed or external hemorrhoids that do not retract on their own or cause significant discomfort
- Persistent itching or burning in the anal region
- Difficulty with bowel movements, such as straining or pain during bowel movements
- Changes in bowel habits, such as diarrhea or constipation that lasts for more than a few days
Causes Of Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids can have multiple causes, which can include:
-
Straining during bowel movements: When you strain during bowel movements, you increase the pressure in the veins in the anal area, which can lead to the development of hemorrhoids.
-
Chronic constipation or diarrhea: These conditions can also lead to hemorrhoids due to the pressure exerted on the veins in the anal area.
-
Sitting for long periods: Sitting for prolonged periods of time, especially on hard surfaces, can put pressure on the veins in the anal area and contribute to the development of hemorrhoids.
-
Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase your risk of developing hemorrhoids due to the extra pressure on the veins in the pelvic area.
-
Pregnancy: Pregnant women are more prone to developing hemorrhoids due to the increased pressure on the veins in the pelvic area, as well as hormonal changes.
-
Age: As you age, the tissues that support the veins in the anal area can weaken, making you more susceptible to developing hemorrhoids.
-
Genetics: Some people may be more prone to developing hemorrhoids due to genetic factors.
Risk factors
Several factors can increase your risk of developing hemorrhoids, including:
-
Age: Hemorrhoids become more common as you age, as the tissues that support the veins in the rectum and anus weaken over time.
-
Genetics: Some people may be more prone to developing hemorrhoids due to genetic factors.
-
Chronic constipation or diarrhea: Straining during bowel movements can put pressure on the veins in the rectum and anus, increasing the risk of developing hemorrhoids.
-
Sitting for long periods: Sitting for prolonged periods of time, especially on hard surfaces, can put pressure on the veins in the rectum and anus, increasing the risk of developing hemorrhoids.
-
Pregnancy: Pregnant women are more prone to developing hemorrhoids due to the increased pressure on the veins in the pelvic area, as well as hormonal changes.
-
Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase your risk of developing hemorrhoids due to the extra pressure on the veins in the pelvic area.
-
Anal intercourse: Engaging in anal intercourse can cause trauma to the anal area, increasing the risk of developing hemorrhoids.
-
Lack of exercise: Lack of exercise can lead to poor circulation, which can increase the risk of developing hemorrhoids.
-
Certain medical conditions: Conditions such as liver disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and chronic heart and lung disease can increase your risk of developing hemorrhoids.
Prevention
There are several steps you can take to prevent hemorrhoids or reduce your risk of developing them:
-
Eat a high-fiber diet: Eating foods that are high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help prevent constipation and reduce the risk of developing hemorrhoids.
-
Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water and other fluids can help prevent constipation and reduce the risk of developing hemorrhoids.
-
Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help improve circulation and prevent constipation, which can reduce the risk of developing hemorrhoids.
-
Avoid sitting for long periods: Taking breaks and standing up and moving around regularly can help reduce the pressure on the veins in the rectal area.
-
Use the bathroom when you need to: Holding in bowel movements can lead to constipation, which can increase the risk of developing hemorrhoids.
-
Avoid straining during bowel movements: Straining during bowel movements can put pressure on the veins in the rectal area, increasing the risk of developing hemorrhoids.
-
Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing hemorrhoids due to the extra pressure on the veins in the pelvic area.
-
Practice good hygiene: Keeping the anal area clean and dry can help prevent irritation and reduce the risk of developing hemorrhoids.
